Sustainability Development Strategies
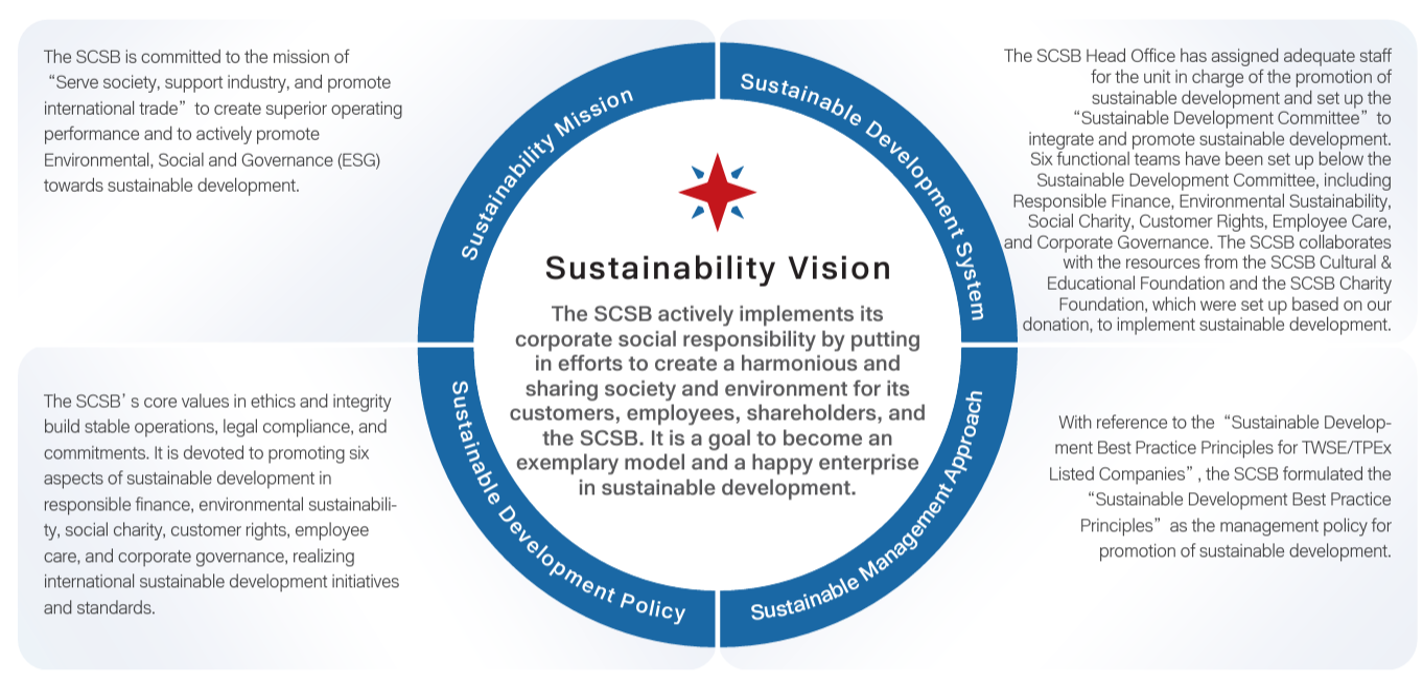
To actively fulfill its corporate sustainability development in line with the international trend of balanced development in the environmental social and corporate governance (ESG), the SCSB has formulated the "Sustainable Development Best Practice Principles" and the "Standard for Sustainable Development Promotion", which contain the mission and vision for sustainable development, sustainable development policy, sustainable development system as well as management policies, and implementation plan. The "Sustainable Development Best Practice Principles" and the "Standard for Sustainability Development Promotion" have been approved by the Board of Directors as the basis and guidelines for the fulfillment of sustainable development.
Sustainability Strategy Structure
Sustainability Development Management
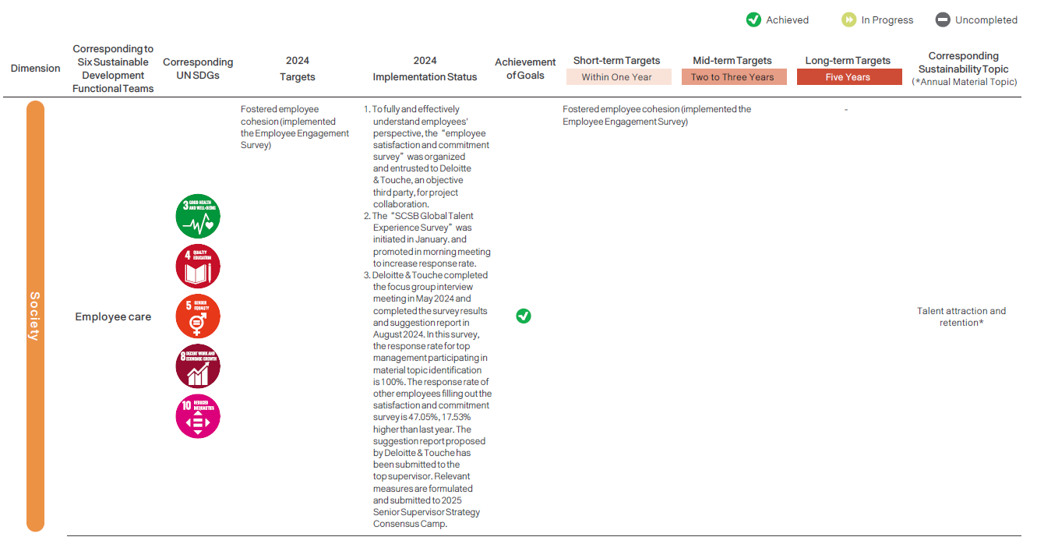
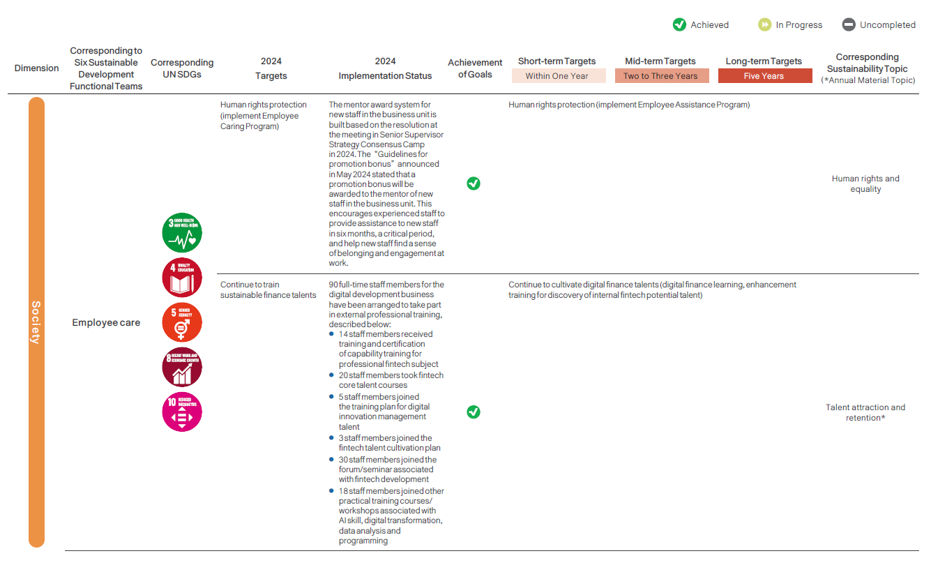
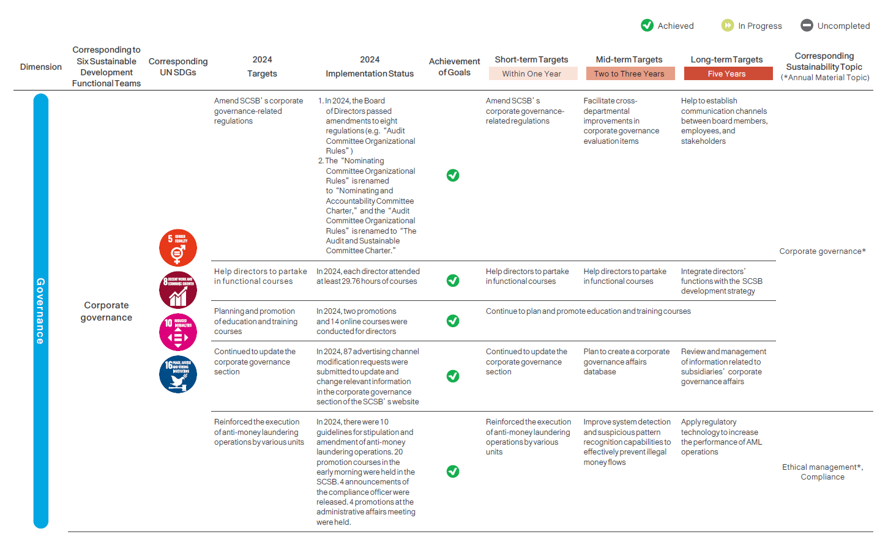
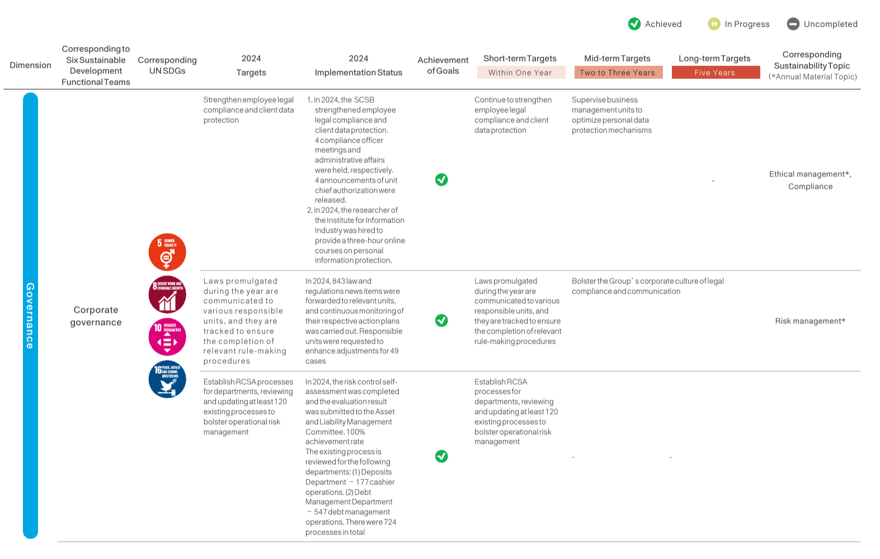
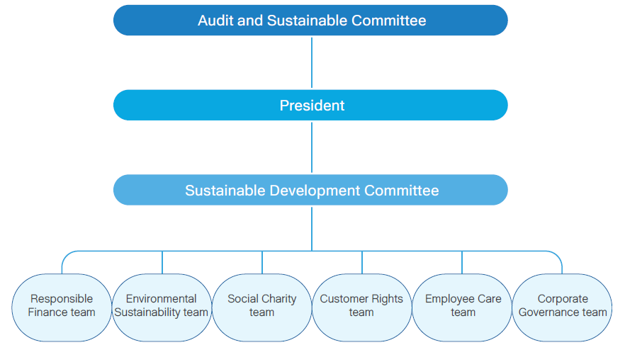
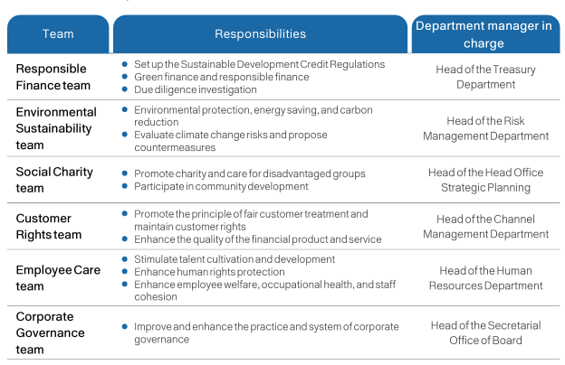
The SCSB has established the “Audit and Sustainability Committee,”, composed of members of the Board of Directors, to serve as the supervisory body and highest decision-making unit for corporate sustainability-related matters. To systematically implement and promote corporate sustainability, the Head Office is in charge of planning sustainable development and compiling the sustainability report, as well as appointing appropriate personnel and formulating the “Regulations for the establishment of the Sustainable Development Committee”. Members include the President (also the convener), Executive Vice Presidents, and departmental heads at all levels. The committee is responsible for planning and reviewing the outcomes of sustainability strategies. Six functional teams including Responsible Finance, Environmental Sustainability, Social Charity, Customer Rights, Employee Care, and Corporate Governance were established. The subcommittees integrate resources from the SCSB Cultural & Educational Foundation and the SCSB Charity Foundation, ensuring that sustainability efforts are implemented effectively throughout the organization. They report to the Board of Directors every year on their operations and relevant agendas.
In 2024, four Sustainable Development Committee meetings were convened to report the progress of the six functional teams, updates on climate risk projects, compilation of the sustainability report, discussions, and resolutions on ESG performance and evaluation, updates and amendments to sustainability policies, sustainable finance evaluation results, progress on green sustainable financing, and planning of renewable energy projects.
The Organizational Chart of Sustainable Development Committee
Work Description


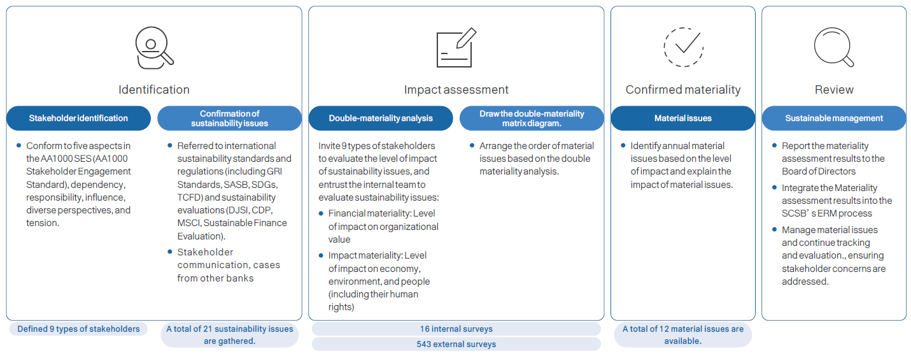
Stakeholder Identification and Engagement
After internal discussion on the survey and reference from other banks on stakeholder identification and engagement, the SCSB identified 9 types of possible stakeholder groups based on the AA1000SES Stakeholder Engagement Standard, government and competent authorities, employees, customers, shareholders and investors, suppliers, financial institutions, organizations associated with communities, organizations associated with environment and media. To understand how each stakeholder evaluates the level of impact of sustainability issues, the SCSB designed a questionnaire and distributed it to the stakeholder groups to be completed. The questionnaire can also be filled out on the SCSB’s website. The results of stakeholder engagement and impact assessment of material issues are reported to the Board of Directors in accordance with the material issue management process and incorporated into the SCSB’s Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) process.
Questionnaire for the Evaluation on the Concern Issues of Corporate Sustainable Development https://eservice.scsb.com.tw/scsbCSR/JSP/scsbCSRSurvey.jsp
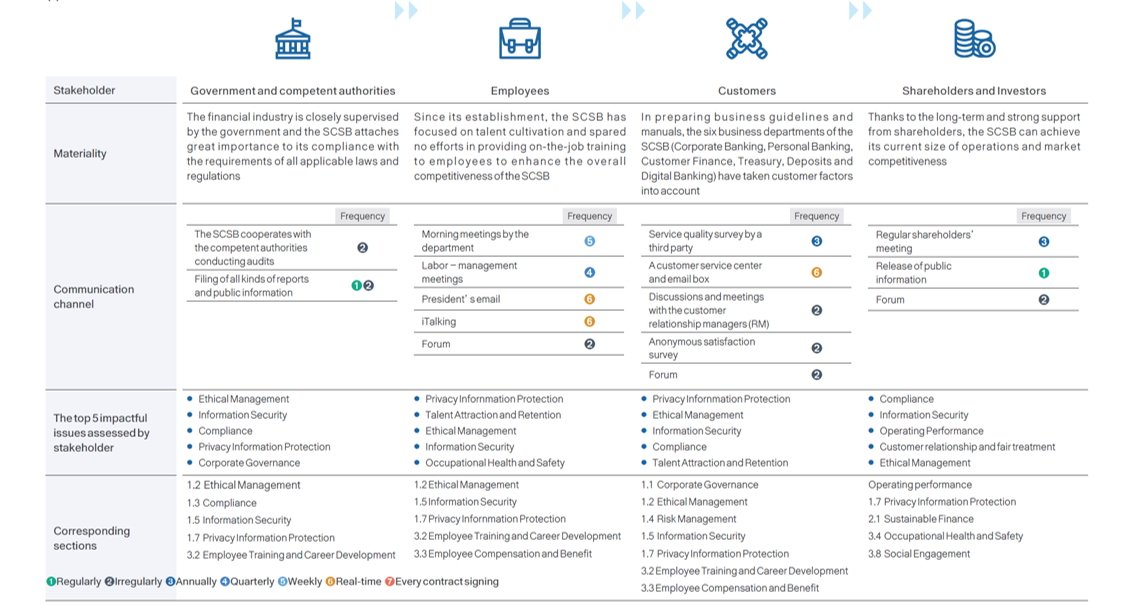
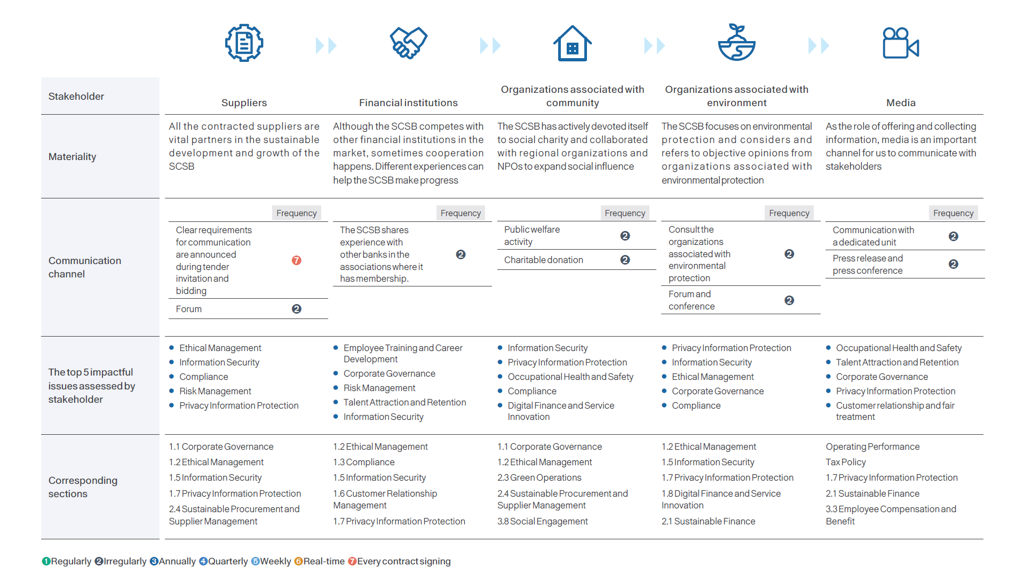
(I) Results of Stakeholder Identification
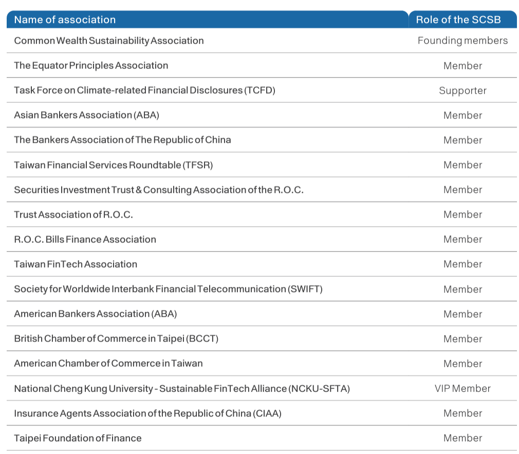
(II) Participation in Industry Associations
In addition to active engagement and negotiation with stakeholders, the SCSB actively participates in key industry associations related to sustainability and finance. Through dialogue and collaboration on material issues, these efforts aim to contribute to the continued stability and responsible development of the financial sector.
The SCSB was invited to fill out the institutions’ surveys such as DJSI, CDP, FTSE and GCBSI, enabling ongoing dialogue and review of key issues. In 2023, the SCSB signed a commitment to the Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi) and received approval in January 2025, pledging to pursue a net-zero transition in line with the goals of the Paris Agreement.

(III) Identification of Material Issues
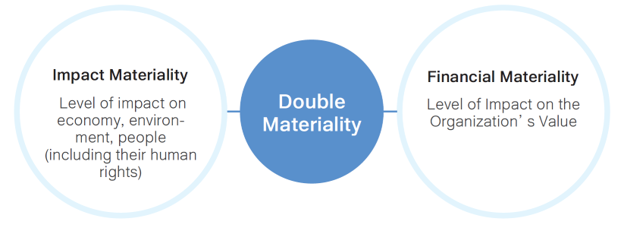
Double-Materiality Analysis
The SCSB conducts an annual materiality assessment and adopts the EU’s “Double Materiality” principle, taking into account both impact materiality and financial materiality in evaluating sustainability material topics. In accordance with GRI 3: Material Topics 2021, the SCSB engaged nine types of stakeholders and internal senior management to assess the actual and potential positive and negative impacts of economic, environmental, and people (including human rights) issues.
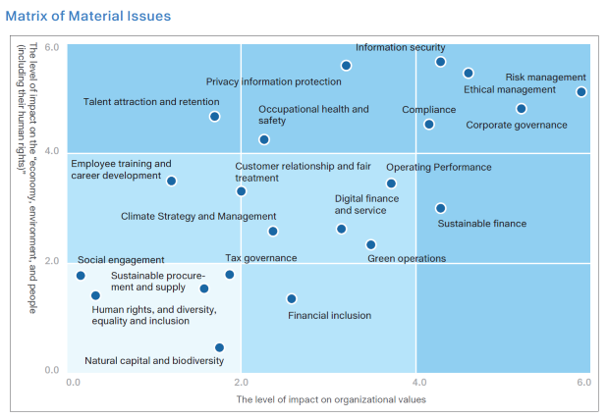
Based on the results of the stakeholder concern survey and the impact severity analysis of sustainability issues, the SCSB held internal discussions to separately evaluate the impact materiality and financial materiality of each topic. A topic is identified as material if it meets the threshold for either dimension of materiality.
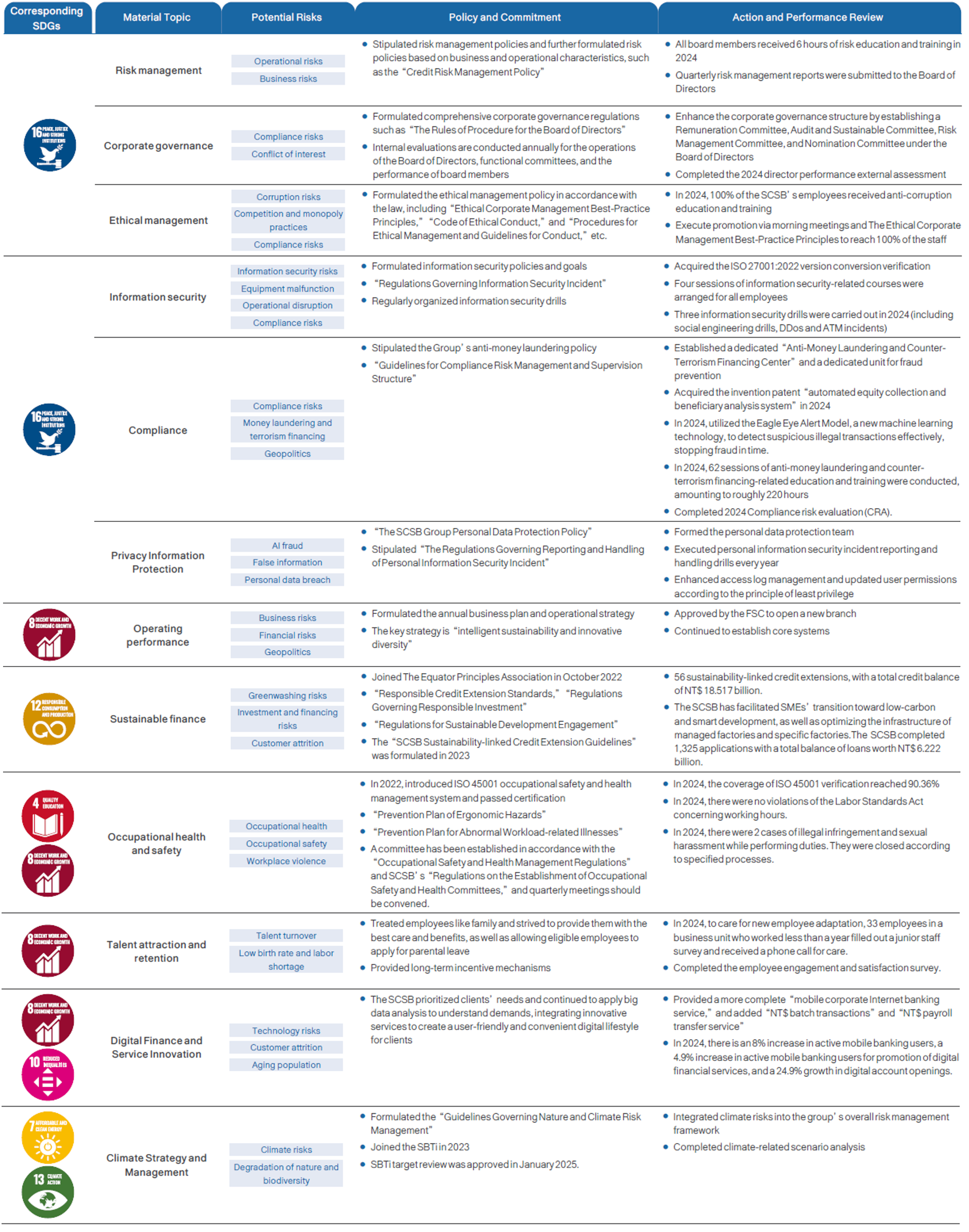
In 2024, 12 material topics were identified, including “Risk Management,” “Corporate Governance,” “Ethical Management,” “Information Security,” “Compliance,” “Privacy Information Protection,” “Operating Performance ,” “Sustainable Finance,” “Occupational Health and Safety,” “Talent Attraction and Retention,” “Digital Finance and Service Innovation” and “Climate Strategy and Management.” Compared with 2023, a material topic “Occupational Health and Safety” was added. “Employee Training and Career Development” was not included in the scope of this year’s material topics.
Looking ahead, the SCSB will continue to communicate with stakeholders via diverse channels to gain a real-time understanding of material topics’ positive and negative impacts on the SCSB, as well as stakeholders’ assessments of the effectiveness of the SCSB’s actions in response to such impacts.
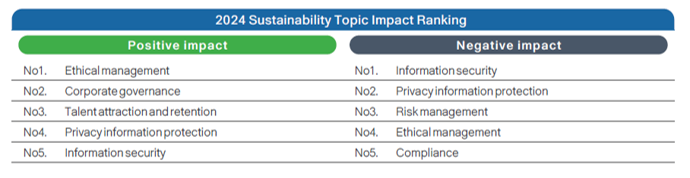
Positive and Negative Impacts of Sustainable Topics
The SCSB further analyzed the positive and negative impacts of each sustainability topic based on the likelihood of occurrence and severity, and ranked the results accordingly.
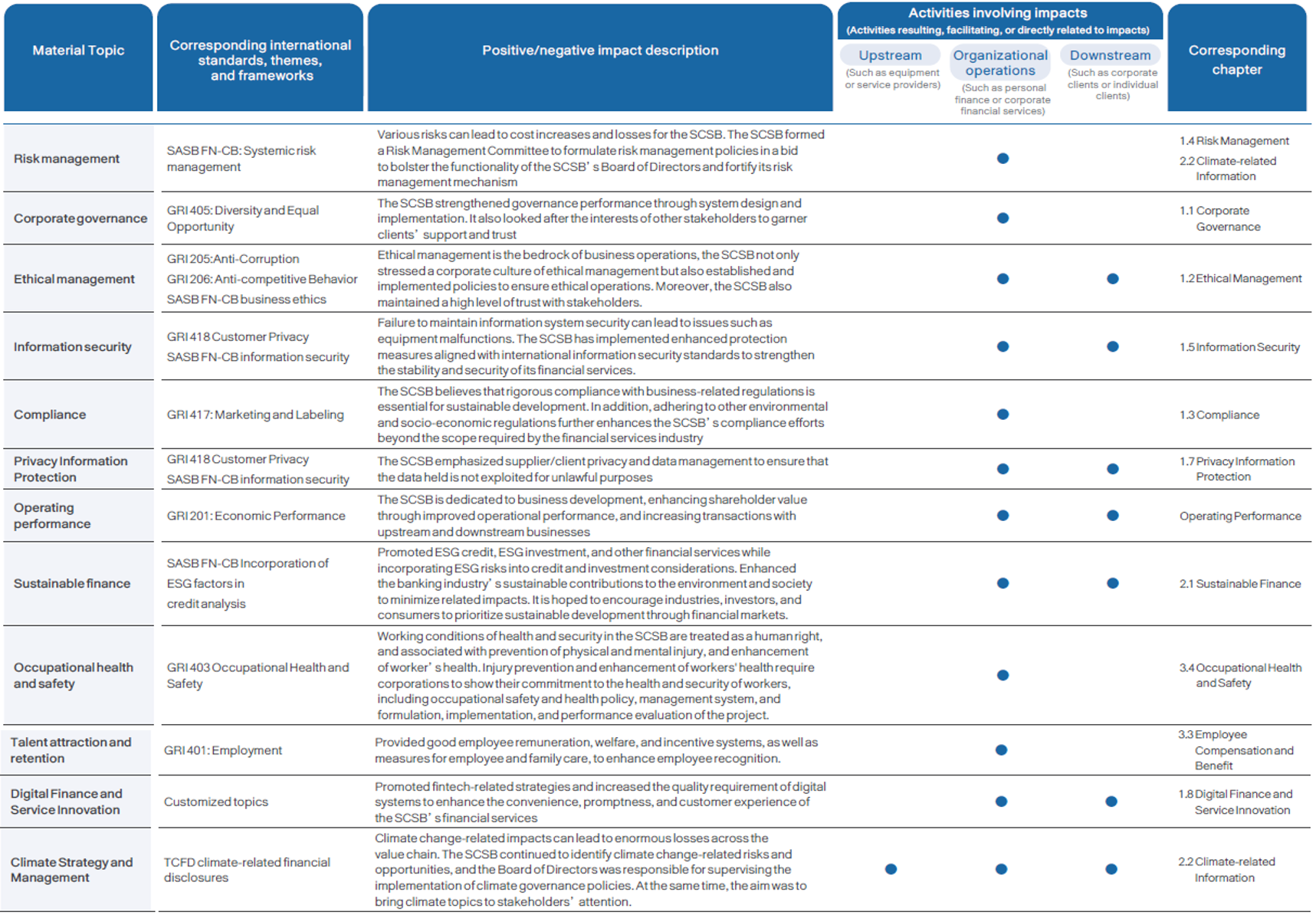
Material Topic Description
Material Topic Management
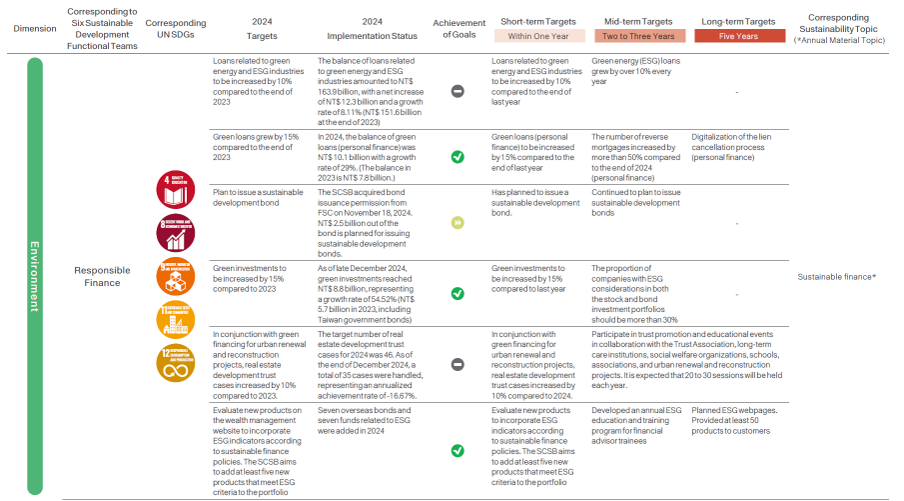
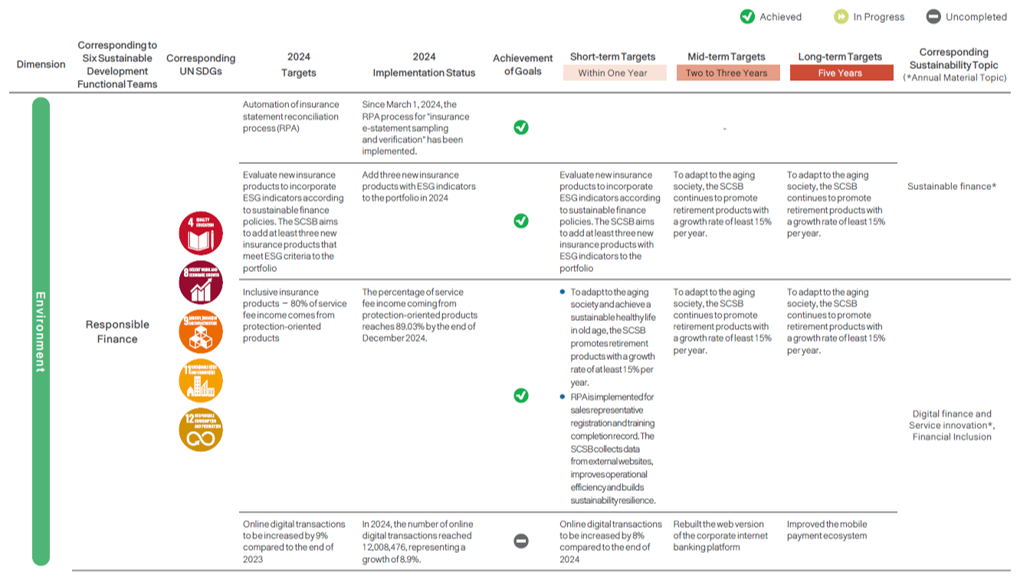
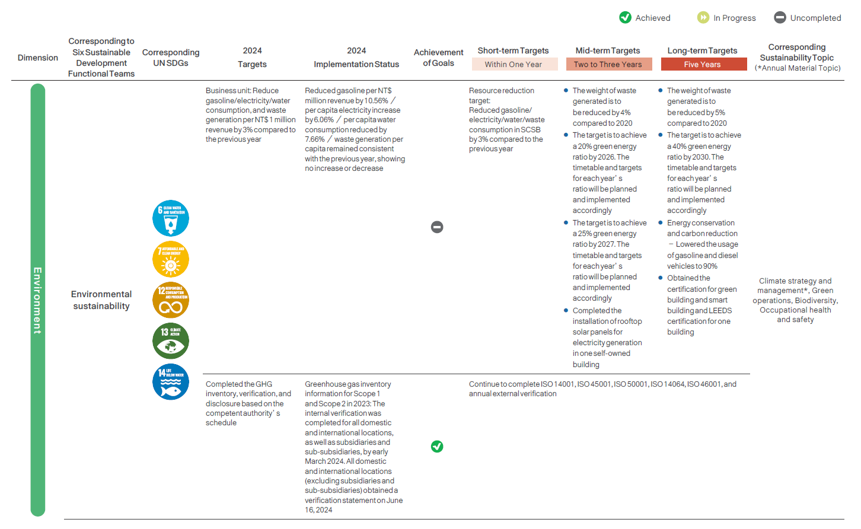
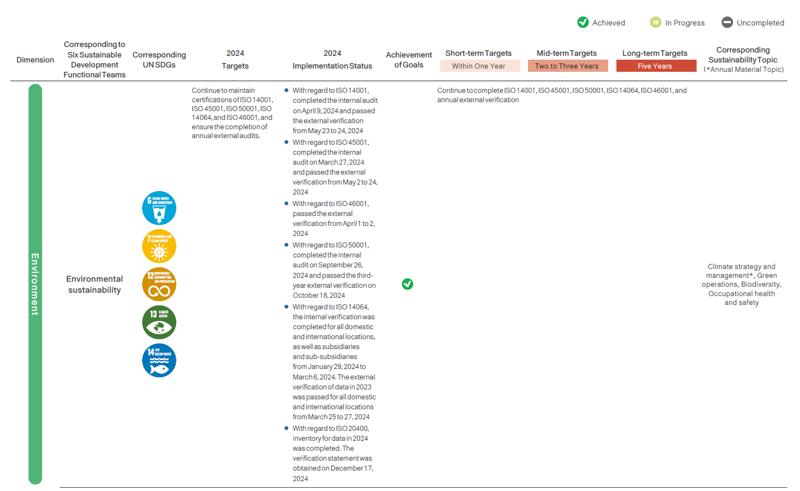
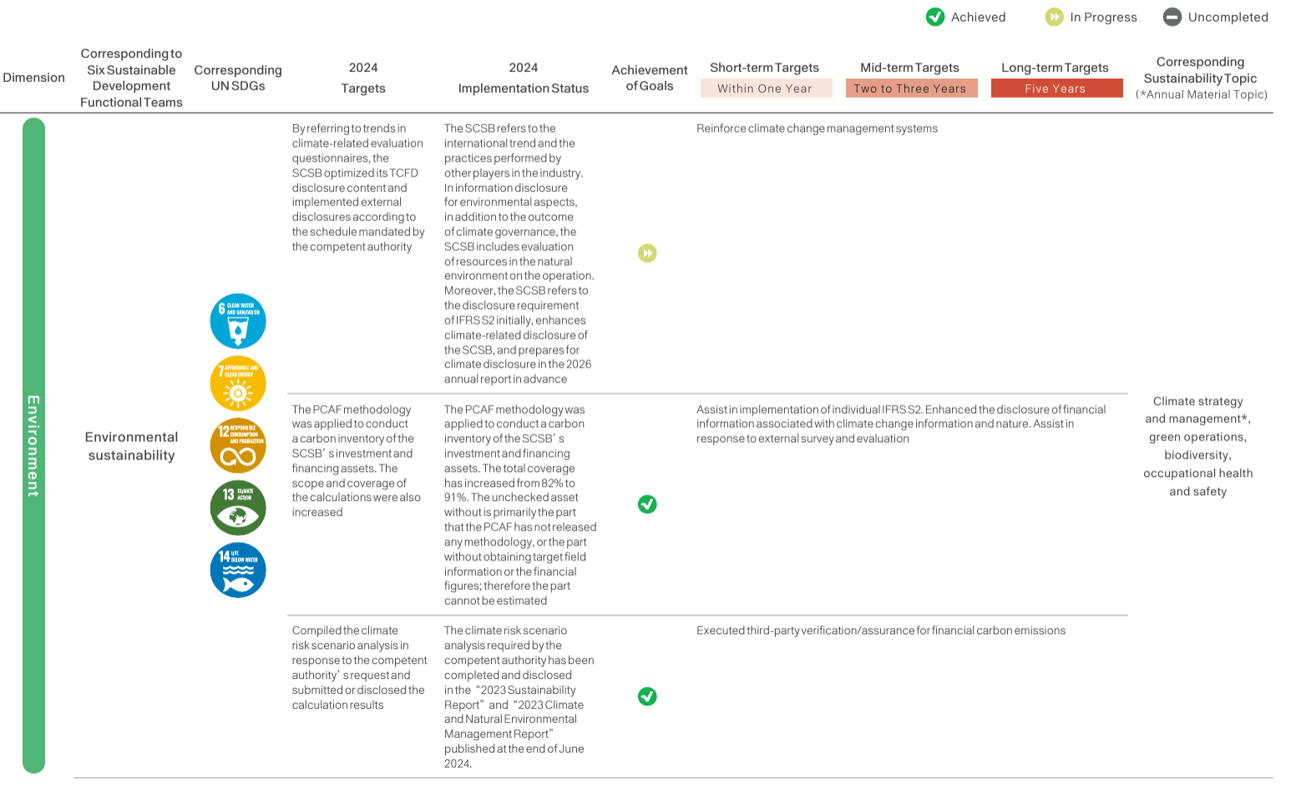
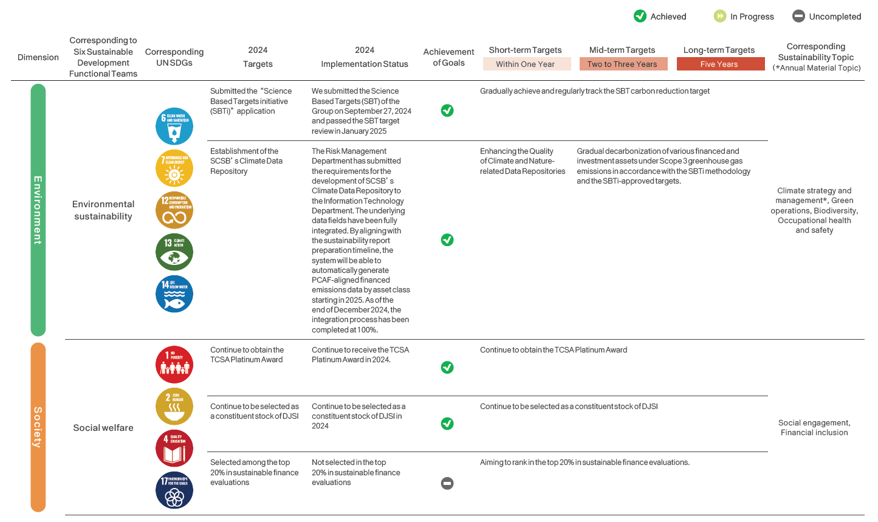
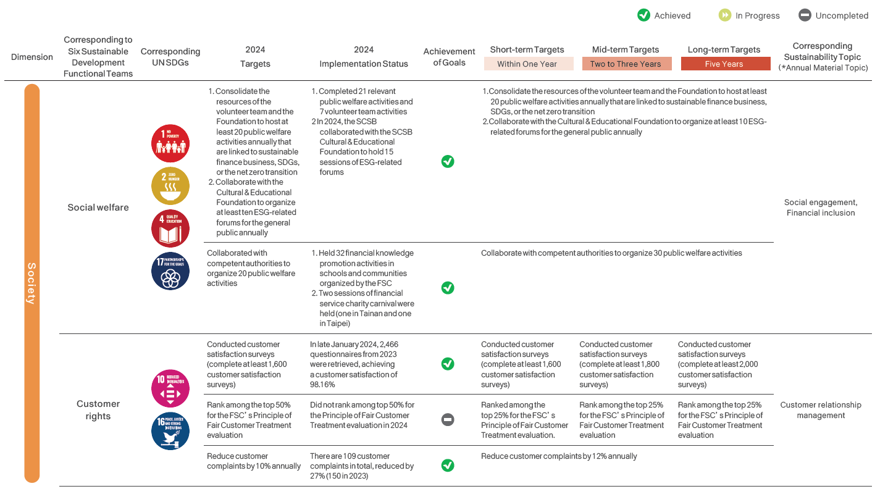
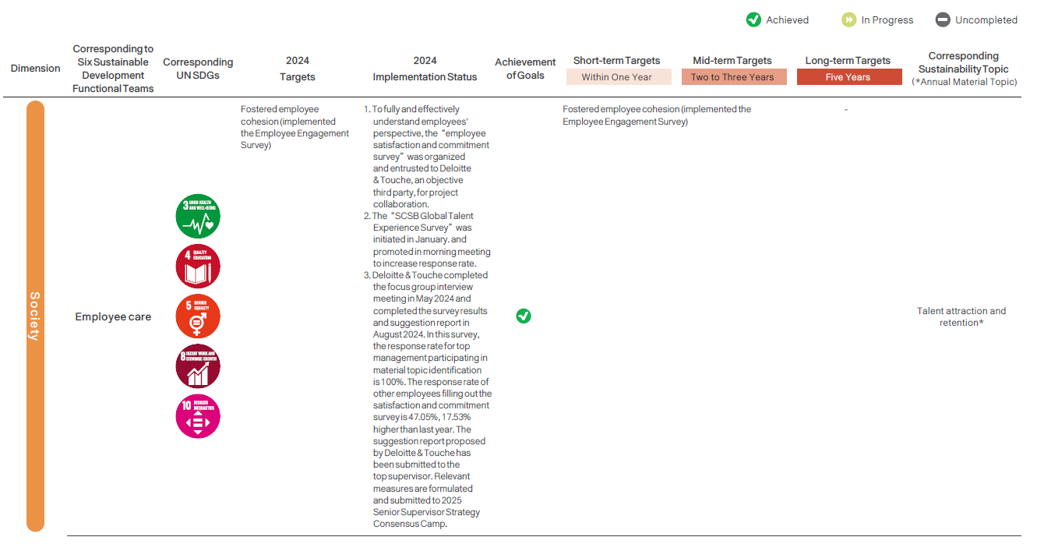
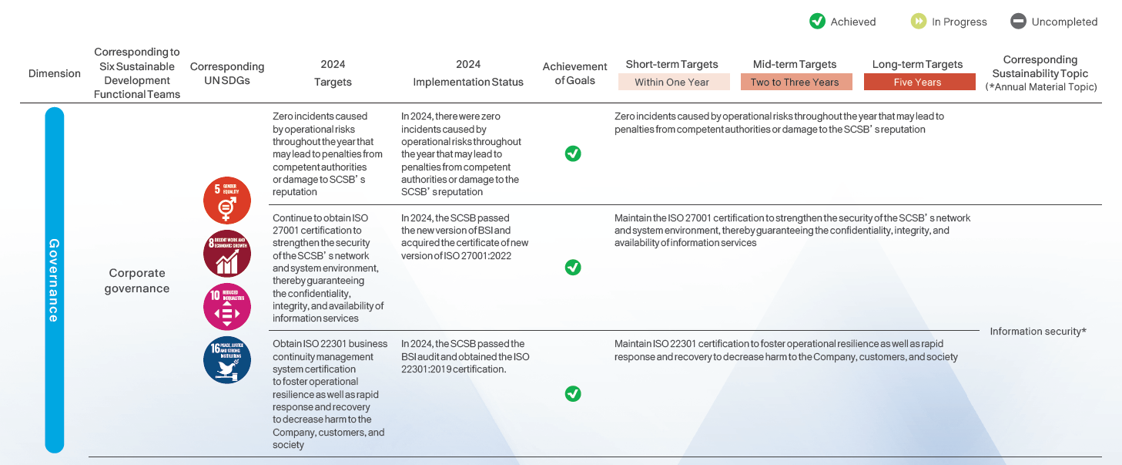
Sustainable Strategic Target Planning